On September 19th, Azerbaijan, a former Soviet republic, initiated military action in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh, which it shares with neighboring Armenia. Spectee Pro provided early updates, including reports of air raid sirens, delivering on-the-ground information faster than mainstream media outlets. Nagorno-Karabakh had witnessed significant military conflicts in 2020 and 2022, resulting in thousands of casualties on both sides. However, in this instance, Armenia refrained from mounting a counteroffensive, effectively leading to Azerbaijan's victory, with a ceasefire agreement reached on the following day, September 20th.
Gunfire echoes through the major city of Hankendi (known as Stepanakert in Armenia)
The ammunition depot belonging to the units of the Armenian armed forces was destroyed.
— Clash Report (@clashreport) September 19, 2023
One of the ammunition depots belonging to the 5th defense brigade of the Armenian armed forces located in the direction of Aghdara was destroyed. pic.twitter.com/qzfeCsZoY4
Why is such a conflict happening? Looking back at history, both of these two countries were part of the Soviet Union. During the Soviet era, there was a region known as Nagorno-Karabakh, which is now part of Azerbaijan, but due to its predominantly Armenian population, it was designated as an "Armenian autonomous region" by the Communist Party of Russia.
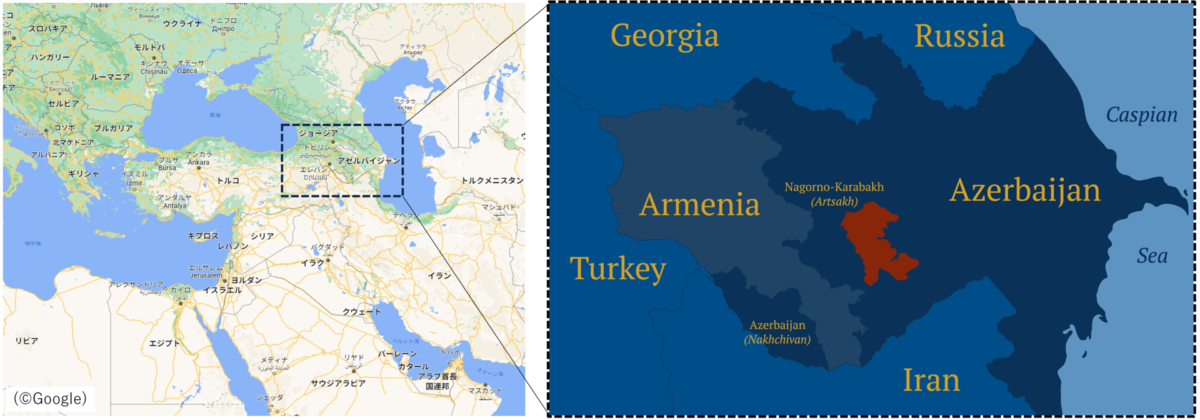
In 1988, the highest authority of the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Region adopted a resolution calling for a change of allegiance from Azerbaijan to Armenia. Armenia supported this move, leading to strong opposition from Azerbaijan and ethnic clashes. In 1991, as the Soviet Union dissolved, both Azerbaijan and Armenia declared their independence. In January 1992, the Armenian forces in Nagorno-Karabakh declared the establishment of their own republic, sparking the ongoing armed conflict. In 1994, Armenian forces established effective control over Nagorno-Karabakh and its surrounding areas, a situation that remained largely unchanged. The Armenian forces operated the region they controlled as the "Republic of Artsakh" and received supplies from Armenia through a route known as the Lachin Corridor. Prior to the recent military activity, Azerbaijan had blockaded this corridor for approximately nine months, leading to shortages of essential supplies such as food and medicine, as reported by Reuters.
The recent conflict quickly subsided, and currently, Armenian residents of Nagorno-Karabakh are evacuating en masse to their home country. According to Reuters, nearly all of the approximately 120,000 Armenian residents wish to relocate. Additionally, on September 28, the President of the Republic of Artsakh signed a decree dissolving all state institutions as of January 1, 2024. This move indicates that Nagorno-Karabakh is returning to Azerbaijan's jurisdiction, potentially signaling the end of the long-standing conflict. On October 5, Armenian Prime Minister Pashinyan and Azerbaijani President Aliyev are scheduled to meet in Granada, southern Spain.
Cars attempting to evacuate are stuck on a road in Hankendi
Stepanakert now. There is an almost 100km line of cars from Nagorno-Karabakh to Armenia as the entire population flees. 120,000 people are leaving their homes. pic.twitter.com/p6rNDz37tl
— Neil Hauer (@NeilPHauer) September 25, 2023
The Caucasus region is indeed known for its complexity in terms of national and ethnic relations, making it prone to conflicts and clashes. It encompasses the Caucasus Mountains, which include peaks exceeding 5,000 meters, serving as a watershed that divides Russia from the Islamic world. Azerbaijan and Armenia share borders with Turkey and Iran, while Georgia to the north has seen recurring military conflicts with Russia, resulting in regions like South Ossetia and Abkhazia being effectively controlled by Russia. Despite its small size, the region's mountainous terrain has led to the existence of various linguistic and ethnic groups, including Slavic-speaking Russians, Iranian-origin Ossetians, Caucasus-based Georgians and Chechens, Armenians with their unique script, and Azerbaijanis of Turkish descent, among others. Furthermore, the region is marked by diverse religions, including Islam (both Sunni and Shia branches) and various branches of Christianity (Orthodox, Eastern Orthodox, Catholic), creating a mosaic of ethnic and religious diversity.
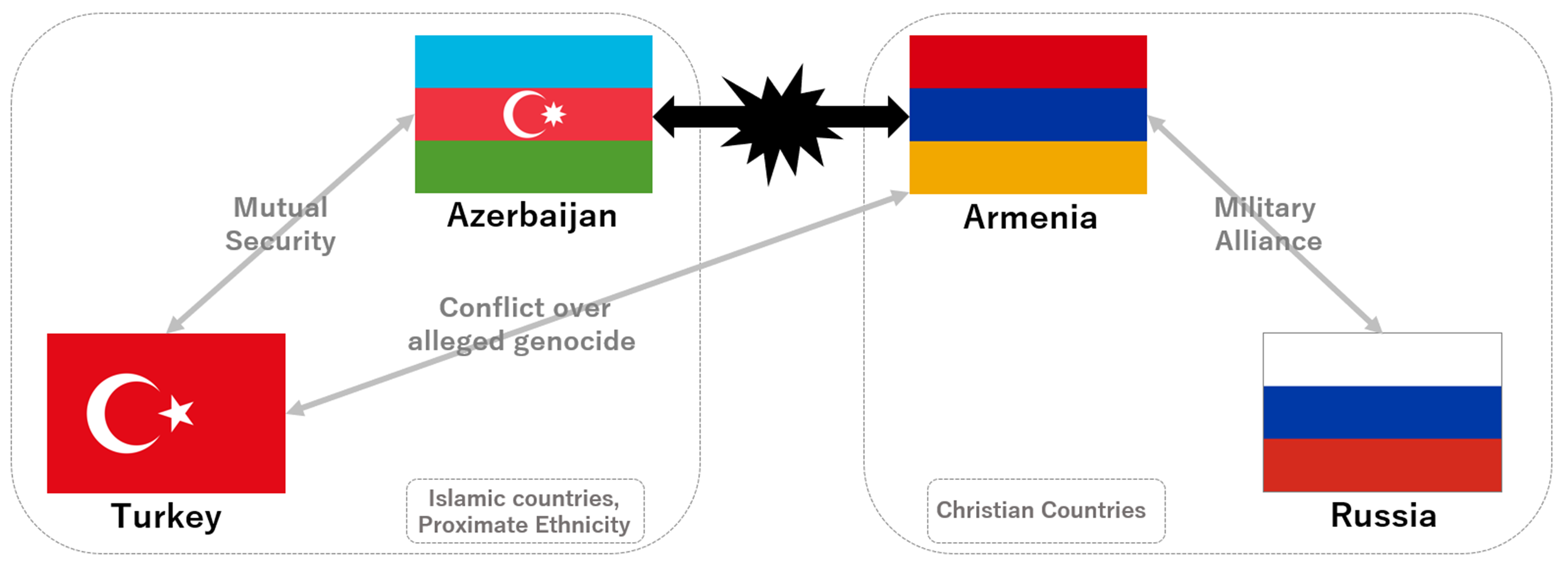
In the Caucasus region, the relationship between Armenia and Azerbaijan had remained relatively stable despite underlying conflicts for many years. However, one significant factor that contributed to the sudden escalation of tensions was the diminishing influence of Russia in the area. As depicted in the map, Azerbaijan had Turkey, a ethnically close ally, as its backer, while Armenia, although a Christian nation like Russia, had Russia as its supporter, creating a certain balance of power. Yet, with Russia weakened due to its involvement in the Ukraine conflict, it was no longer in a position to intervene in the conflicts in this region. This assessment likely played a role in Azerbaijan's decision to launch this military operation.On the other hand, Armenia, as a member of the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO), a military alliance led by Russia, was in a complicated situation. Despite its CSTO membership, Armenian Prime Minister Pashinyan hinted at the possibility of withdrawing from the organization and sought closer ties with the United States. The waning influence of Russia in the region certainly contributed to the current situation.
While conflicts in the Caucasus region may not have a direct impact on Japan, it's essential to focus on the backdrop of "Russia's weakening influence." Changes in the balance of power in various regions could lead to increased geopolitical risks. Questions arise about how Central Asia will align itself, whether India, closely tied militarily with Russia, will adjust its strategy, and what will happen to the situation in West Africa, where Russia had been increasing its influence. Analyzing geopolitical risks while considering various scenarios becomes crucial in light of Russia's diminishing centrality in global affairs.
Satoshi Negoro
September 11, 2023
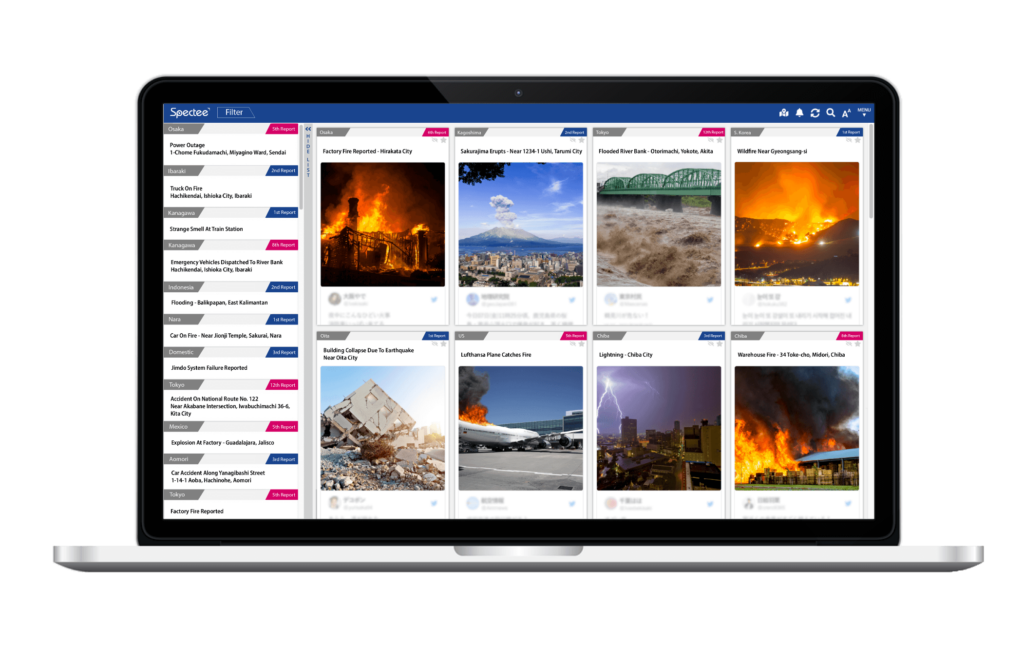
Cloud-based AI Solution for Disaster Prevention and Risk Management “Spectee Pro” ( https://www.spectee.com/spectee-pro/) provided by Spectee is used by many local governments, private companies and the media.With its flexibility, accuracy, and comprehensiveness, it is possible to “grasp the damage situation in the event of a crisis faster and more accurately than anywhere else.”
Utilizing AI to analyze information, from information posted on SNS such as Twitter and Facebook, more than 100 events such as emergency information such as natural disasters, fires and accidents, information on infectious diseases, etc. , airports, stations, commercial facilities, and sightseeing spots, you can check “what is happening where” in real time.
Contact: https://www.spectee.com/contact-us/